If you are searching for “what does a torque converter do“, this article will cover how it works, its components, pricing and common problems.
How Torque Converters Work
If you currently have an automatic transmission vehicle, then you already use torque converters daily. These converters are some of the most complex parts in the internal areas of your vehicle. The engine connects to the transmission with a clutch, so the vehicle can come to a full stop without harming the engine. Vehicles that feature an automatic transmission have something else that connects the engine to the transmission: a torque converter.
You will find this doughnut-shaped component attached directly between the transmission and engine. Two series of curved blades, facing opposite directions, work inside the converter. The inside will be filled with transmission fluid that helps transfer power from the engine to the transmission. Torque converters generally work with maximum efficiency by generating as much energy transmission as possible, while reducing any heat buildup.
Where a manual transmission vehicle makes use of a clutch, an automatic transmission vehicle substitutes that with a torque converter for the same purpose.
In order for the vehicle to operate it is important that the engine is linked to the rear wheels through such a mechanism that it can be connected so that the vehicle moves or disconnected so that it will stay motionless while the engine runs to provide other functions.
Manual vehicles make use of the clutch to link and delink the transmission from the engine, and automatic vehicles use a fluid mechanism like the torque converter sitting in between the transmission and the engine.
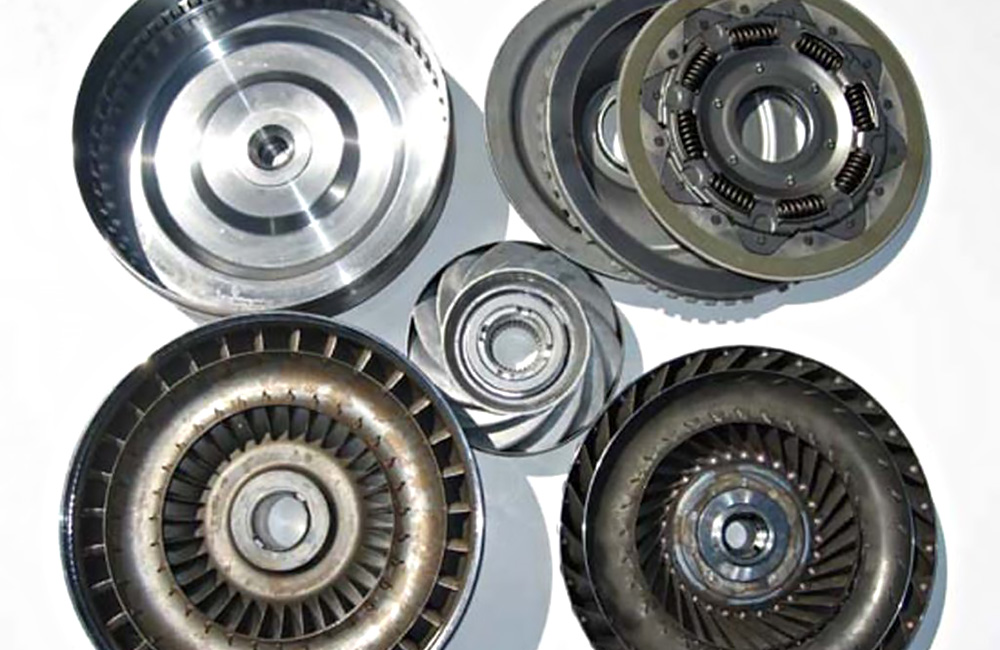
Torque Converter Components
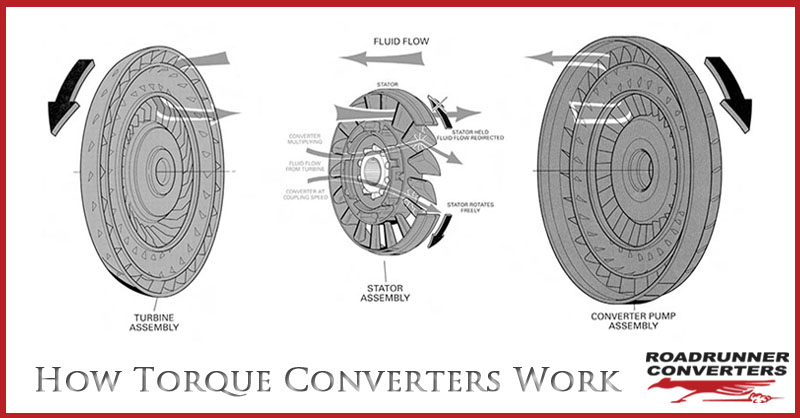
A torque converter comprises of three key components inside its shell, the Pump, the Turbine, and the Stator that coordinate power transmission from the engine to the transmission.
The centrifugal pump inside the torque converter spins the fluid to the outside, very similar to what a spinning cycle of a washing machine would do. This action of the fluid being flung towards the outside creates a vacuum drawing more fluid towards the center.
When this fluid reaches the turbine, which is linked with the transmission through the middle spline, the blades move causing the transmission to spin, and that in turn moves the vehicle. The turbine uses curved blades to change the direction of the fluid that enters so that it flows through the center of the turbine, and this change in direction enables the turbine to spin.
The fluid leaves the turbine through the center, flowing in a completely different direction to when it entered, and opposite the direction the engine and pump are turning in. If this motion does not occur and the fluid hits the pump, it will slow down the engine and waste power. This is where the third component of the converter, the stator, comes in play.
The stator sits right at the center of the torque converter, redirecting the fluid that returns from the turbine to stop it from hitting the pump again. This action adequately increases the torque converter’s efficiency.
Torque Converter Replacement Cost
Costs for a professional torque converter replacement can vary based on the labor rate at automotive shop locations. Labor costs should run between $400 and $700 at most shops. The total price for parts and labor should range from $600 to around $1,000. If this seems too costly, doing the replacement yourself remains an option, and cheaper alternative. The average cost for a DIY replacement is $400, while a typical average cost for a professional service is around $850. At the time of a torque converter replacement, a change of the transmission fluid is recommended. Transmission flush costs range from $125-$250.
Torque Converter Problems
Several issues can arise as a torque converter gets older and experiences some wear and tear. High levels of slippage can cause these parts to overheat. This can also damage the elastomer seals that keep the fluid inside the converters. If you happen to notice that the converter is not working as efficiently as it once was, it is possible that the part is experiencing some blade fragmentation and/or deformation. Your car’s gas mileage dwindling is a warning sign that this may be occurring.
The stator clutch can break, at times. If certain elements of the clutch become permanently locked, you’ll experience a large drop in fuel efficiency. If the clutch completely breaks off, the vehicle may have trouble moving under its own power.
Road Runner Converters Offers Many Torque Converter Replacements
Road Runner Converters offers many torque converters for sale online. We offer GM Torque Converters, Ford Torque Converters, Diesel Torque Converters, Towing Torque Converters, Street Torque Converters and more.